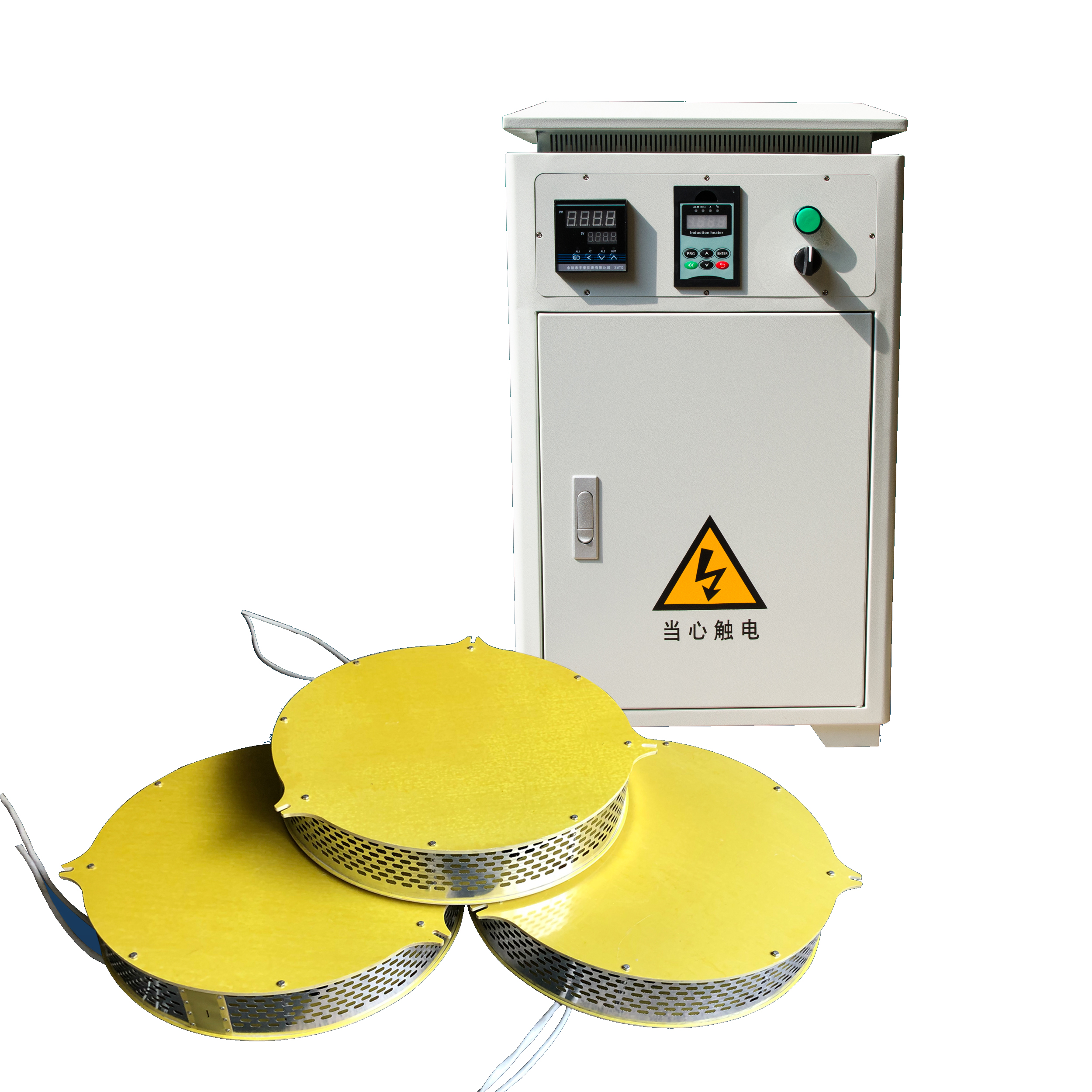
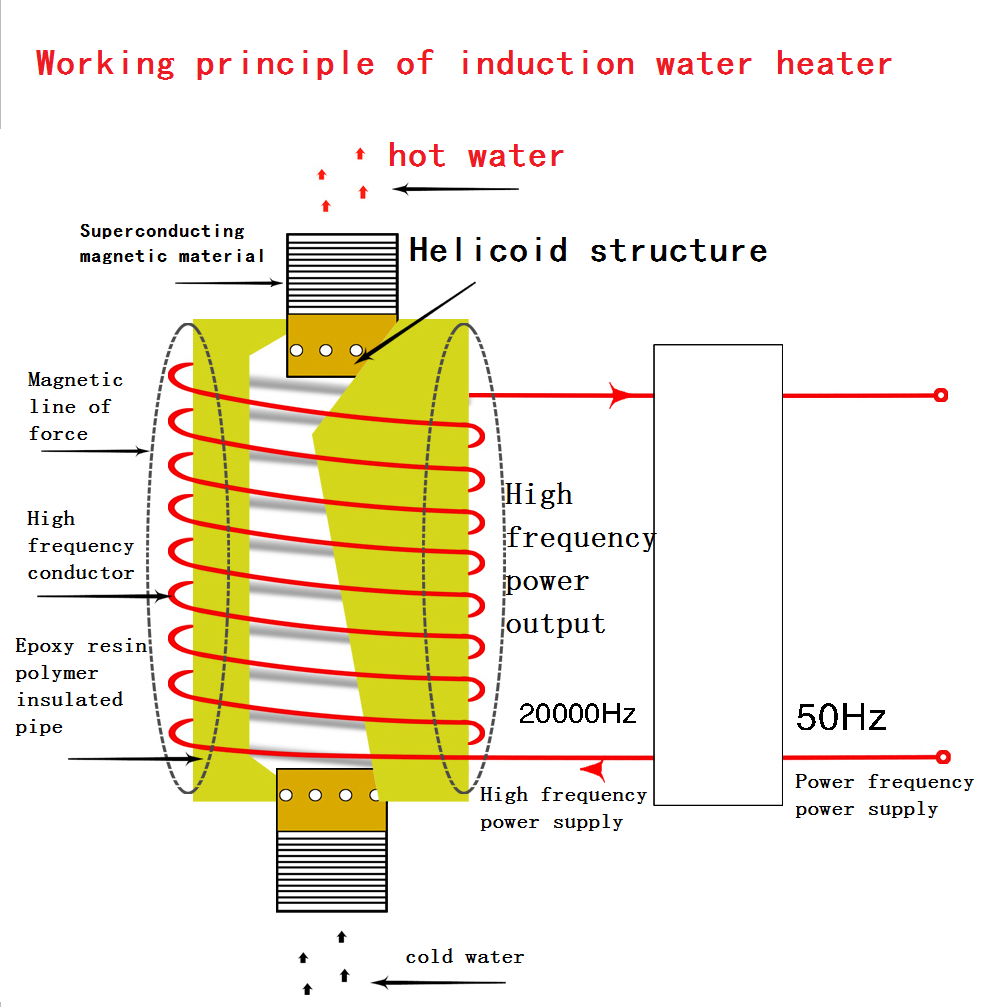
Induction heating applied to room heating represents a relatively novel approach compared to traditional methods like forced air, radiators, or infrared heaters. This technology, predominantly used in industrial applications and cooking, can also offer several advantages for residential and commercial space heating. Here’s how it could work and the benefits it might provide:

How Induction Heating Works for Room Heating
Induction heating operates on the principle of electromagnetic induction, where an electric current generates a magnetic field that produces heat. In room heating applications, this could involve:
1.Inductive Floor Panels: Installing panels under the floor that contain coils through which alternating currents are passed. The magnetic field generated by these currents would heat the metallic elements embedded within the floor structure, which in turn would radiate heat upwards into the room.
2.Wall-Mounted Induction Units: Similar to radiators, but using induction coils to generate heat that warms the air directly or heats up a secondary element that radiates heat.
Benefits of Induction Heating in Room Heating
3.Efficiency: Induction heating is highly efficient as it converts almost all the electrical energy into heat with minimal losses, unlike conventional heating methods that can be inefficient and costly.
4.Rapid Heating: The process can heat spaces quickly because it generates heat directly and instantaneously within the heating element or medium, rather than slowly warming air or water as in traditional systems.
5.Zonal Heating Control: Induction heating systems can be designed to provide targeted heating to specific zones within a building, reducing energy waste and improving comfort.
6.Low Maintenance: With fewer moving parts than systems like furnaces and without the need for ducts or pipes, induction heating systems require less maintenance.
7.Improved Air Quality: Unlike forced-air systems that can circulate dust and allergens, induction heating does not move air, thereby potentially improving indoor air quality.
8.Safety and Comfort: Induction heating does not produce open flames or hot surfaces that are accessible, which can be safer in homes with children and pets. It also does not dry out the air as much as conventional heaters.
Challenges and Considerations
9.Cost: The initial setup cost for induction heating systems can be higher than traditional heating methods, due to the technology and installation requirements.
10.Implementation: Retrofitting existing buildings with induction heating systems might be challenging and expensive, more suited for new constructions or major renovations.
11.Public Awareness and Skill: Since induction heating in residential heating is not widely used, there might be a lack of skilled professionals for installation and maintenance, and a general lack of consumer awareness about the benefits and operation of the system.
12.Electrical Load: Depending on the size of the space and the climate, induction heating systems might require significant electrical infrastructure, which could be a constraint in areas with limited electrical service capacity.
While still not a mainstream solution for room heating, induction heating presents an innovative option that could become more viable as technology advances and as energy efficiency becomes a greater priority in building design and operation.